Crafting has undergone a remarkable transformation throughout history, evolving from a necessity for survival into a cherished form of artistic expression. In ancient times, crafting was primarily utilitarian; early humans fashioned tools, clothing, and shelter from available materials to meet their basic needs. As societies progressed, so too did the complexity and variety of crafts.
The advent of agriculture allowed for more leisure time, which in turn fostered creativity. This shift gave rise to intricate pottery, textiles, and metalwork, reflecting the cultural values and technological advancements of the time. The Industrial Revolution marked a significant turning point in the world of crafting.
Mass production began to dominate, leading to a decline in traditional handcrafts as factory-made goods flooded the market. However, this period also sparked a counter-movement that celebrated craftsmanship and the handmade. The Arts and Crafts Movement emerged in the late 19th century, advocating for the value of skilled artisanship and the beauty of handcrafted items.
This resurgence laid the groundwork for contemporary crafting practices, which now blend traditional techniques with modern aesthetics, allowing artisans to explore new materials and methods while honouring their heritage.
Summary
- Crafting has evolved from traditional methods to include modern techniques and materials, reflecting changes in society and technology.
- Technology has revolutionised crafting, making it more accessible and allowing for greater creativity and innovation.
- Sustainable crafting practices are becoming increasingly important, with a focus on using eco-friendly materials and reducing waste.
- Crafting has been shown to have a positive impact on mental health and wellbeing, providing a therapeutic outlet for stress and anxiety.
- Crafting allows individuals to express their creativity and personality, providing a means of self-expression and personal fulfilment.
- Many people have turned their crafting hobbies into successful businesses, selling handmade products and services.
- Crafting is increasingly being recognised as a valuable educational tool, promoting creativity, problem-solving, and practical skills.
- Crafting holds cultural significance, preserving traditional techniques and providing a means of cultural expression and identity.
The Impact of Technology on Crafting
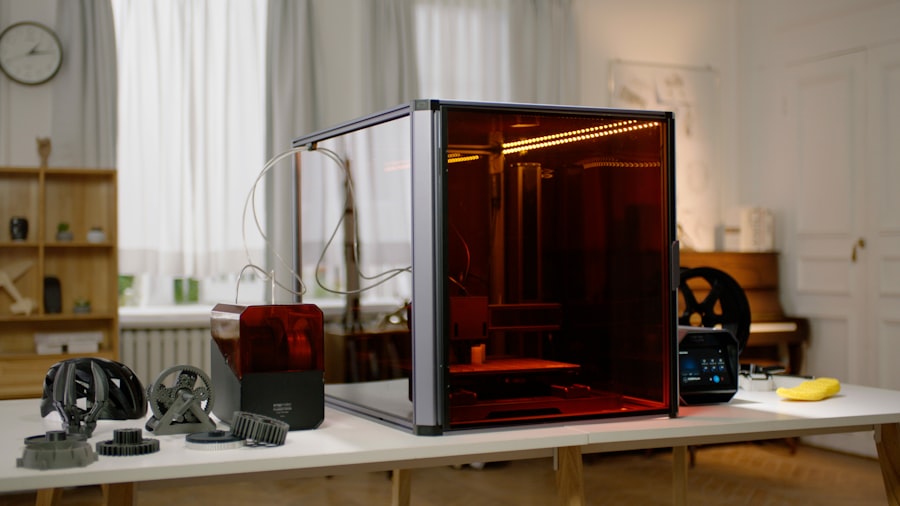
In recent years, technology has profoundly influenced the landscape of crafting, introducing innovative tools and techniques that have expanded creative possibilities. The rise of digital fabrication technologies, such as 3D printing and laser cutting, has revolutionised how artisans approach their work. These tools enable crafters to create intricate designs with precision and efficiency, allowing for a level of detail that was previously unattainable.
Moreover, technology has facilitated the sharing of knowledge and skills through online platforms, enabling crafters from around the globe to connect, collaborate, and inspire one another. However, the integration of technology into crafting is not without its challenges. While digital tools can enhance creativity, they may also lead to a disconnect from traditional crafting methods.
Some purists argue that reliance on technology diminishes the authenticity and tactile nature of handmade items. Nevertheless, many contemporary crafters find ways to harmoniously blend traditional techniques with modern technology, creating unique pieces that honour both heritage and innovation. This fusion not only enriches the crafting experience but also opens up new avenues for artistic exploration.
Sustainable Crafting Practices
As awareness of environmental issues grows, sustainable crafting practices have gained prominence within the crafting community. Artisans are increasingly recognising the importance of using eco-friendly materials and methods that minimise waste and reduce their carbon footprint. This shift towards sustainability is not merely a trend; it reflects a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness between crafting and the environment.
By sourcing materials locally or repurposing discarded items, crafters can create beautiful works while contributing to a more sustainable future. Moreover, sustainable crafting practices often encourage a slower approach to making, promoting mindfulness and intentionality in the creative process. This philosophy stands in stark contrast to the fast-paced consumer culture that dominates much of modern life.
By prioritising quality over quantity and valuing the stories behind materials, crafters can cultivate a deeper connection to their work and the world around them. This movement towards sustainability not only benefits the environment but also fosters a sense of community among artisans who share similar values.
The Role of Crafting in Mental Health and Wellbeing
Crafting has long been associated with therapeutic benefits, providing individuals with an outlet for self-expression and creativity. Engaging in hands-on activities can serve as a form of mindfulness, allowing crafters to focus their attention on the present moment while alleviating stress and anxiety. The repetitive motions involved in many crafts can induce a meditative state, promoting relaxation and mental clarity.
As such, crafting has become an increasingly popular tool for mental health professionals seeking alternative therapies for their clients. Furthermore, the social aspect of crafting cannot be overlooked. Many individuals find solace in joining crafting groups or workshops where they can connect with like-minded individuals.
These communal spaces foster a sense of belonging and support, which can be particularly beneficial for those struggling with feelings of isolation or loneliness. By sharing their skills and experiences, crafters create a nurturing environment that encourages personal growth and emotional resilience. In this way, crafting transcends mere hobby; it becomes a vital component of holistic wellbeing.
Crafting as a Form of Self-Expression
At its core, crafting is an intimate form of self-expression that allows individuals to communicate their thoughts, feelings, and identities through tangible creations. Each piece crafted carries the unique imprint of its maker’s personality and experiences, serving as a reflection of their inner world. Whether through painting, knitting, woodworking, or any other medium, artisans have the opportunity to explore their creativity and convey messages that resonate with themselves and others.
The freedom inherent in crafting empowers individuals to experiment with different styles and techniques without the constraints often found in more formal artistic practices. This sense of liberation encourages risk-taking and innovation, allowing crafters to push boundaries and discover new facets of their creativity. As they navigate their artistic journeys, many find that their crafted pieces become not only expressions of their individuality but also vehicles for storytelling—sharing narratives that connect them to their heritage or address contemporary issues.
Crafting as a Business

In recent years, there has been a notable rise in the number of artisans turning their passion for crafting into viable businesses. The proliferation of online marketplaces has made it easier than ever for crafters to showcase their work to a global audience. Platforms such as Etsy have empowered countless individuals to transform their hobbies into successful enterprises, allowing them to earn a living while doing what they love.
This shift has not only provided financial opportunities for artisans but has also contributed to a growing appreciation for handmade goods. However, transitioning from hobbyist to entrepreneur presents its own set of challenges. Crafters must navigate the complexities of marketing, pricing, and customer service while maintaining their creative integrity.
Balancing artistic vision with commercial viability can be a delicate dance; many artisans grapple with the tension between producing work that resonates with them personally and meeting market demands. Nevertheless, those who successfully carve out their niche often find immense satisfaction in sharing their creations with others while fostering a sense of community around their brand.
The Future of Crafting in Education
As society increasingly recognises the value of creativity in education, crafting is poised to play an integral role in shaping future curricula. Educational institutions are beginning to incorporate hands-on crafting experiences into their programmes as a means of fostering critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and collaboration among students. By engaging in crafting activities, learners can develop not only technical skills but also emotional intelligence as they navigate challenges and celebrate successes together.
Moreover, integrating crafting into education promotes inclusivity by providing diverse avenues for self-expression. Students who may struggle with traditional academic subjects often find solace in creative pursuits where they can excel and build confidence. This holistic approach to education acknowledges that learning extends beyond textbooks; it encompasses experiential knowledge that nurtures well-rounded individuals prepared to thrive in an ever-changing world.
The Cultural Significance of Crafting
Crafting holds profound cultural significance across societies worldwide, serving as a means of preserving traditions and fostering community identity. Many crafts are steeped in history, passed down through generations as families share techniques and stories that connect them to their ancestry. These practices not only honour cultural heritage but also provide opportunities for dialogue between generations as artisans adapt traditional methods to contemporary contexts.
Furthermore, crafting can act as a powerful tool for social change by addressing pressing issues within communities. Artisans often use their skills to raise awareness about social justice or environmental concerns through their work. By creating pieces that provoke thought or inspire action, crafters contribute to broader conversations about identity, belonging, and responsibility within society.
In this way, crafting transcends individual expression; it becomes a collective endeavour that unites people around shared values and aspirations. In conclusion, crafting is an ever-evolving practice that reflects our changing world while remaining deeply rooted in tradition. From its historical origins to its contemporary significance in mental health and education, crafting continues to inspire individuals across cultures and generations.
As we look towards the future, it is clear that this timeless art form will remain an essential part of our collective human experience—one that celebrates creativity, community, and connection.
Crafting the Future explores the innovative techniques and materials used in contemporary art, such as cast paper. For a deeper understanding of this unique art form, readers may be interested in reading An Introduction to the Art Technique Cast Paper. This article delves into the history and process of creating art using cast paper, shedding light on the intricate craftsmanship involved. By learning about different art techniques like cast paper, one can gain a greater appreciation for the creativity and skill that goes into producing modern artworks.


